I was trying to build
my windows workstation using automation and this time decided to use chef as
the CM tool and play around with it. I have used PowerShell DSC to configure my
desktop and was trying to see how Chef can be used also. Below are the steps
that I followed to get it up and running. Hope this gives you an overview on
the process and help you to rebuild your machine also in code!!!
Step 1: Setup the chef development
kit on the machine
The first step is to install the chef development kit and we can use the powershell package manager for this.
Step 2: Create a chef repository
A chef repo is the
directory structure that chef client understands and find related items when we
are working with the chef client. The chef development kit has a generate
command that can be used to create a repository. In the PowerShell prompt type
the command
Chef generate repo
chef-workstation
This will create a
folder chef-workstation under the current path and provision the default files
and folder structure.
You can inspect the structure
of the repository using your favorite editor by opening the root folder. I’ve
used visual studio code to explore the file contents
Step 3: Create our first cookbook
We can use the
generate command to create a cookbook in our repository. Before running the command,
switch to the cookbooks folder in your repo and type in
Chef generate cookbook
windowsdev
Step 4: Add some metadata for the
cookbook
In Visual studio code,
open the metadata.rb file under the windowsdev cookbook folder and update the
metadata as given below.
name 'windowsdev'
maintainer 'Prajeesh Prathap'
maintainer_email 'prajeesh.prathap@infosupport.com'
license 'all_rights'
description 'configures a windows development machine
for .net development'
long_description 'configures a windows development
machine for .net development'
version '0.1.0'
depends 'windows'
depends
'chocolatey'
Note that I have added a dependency for the chocolatey
and windows cookbook in the metadata. We will later use the resources from this
cookbook to install packages from chocolatey on the node.
The windows and chocolatey
cookbooks are available in the chef supermarket and will be used when the
dependencies are needed.
Step 5: Create a recipe
As I mentioned in the
earlier step, we will be using chocolatey to setup the packages on the machine.
Before using chocolatey, we need to first ensure that chocolatey is installed
on the workstation. To install chocolatey, we will create a recipe and use that
in the cookbook before we apply any packages.
Navigate to the
windowsdev cookbook folder and type in the command
Chef generate recipe
setupchoco
Open the newly created
recipe file in the editor and add the contents given below.
#
# Cookbook Name:: windowsdev
# Recipe:: setupchoco
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 Prajeesh Prathap, All Rights
Reserved.
# Configures chocolatey on the machine
include_recipe 'windows'
chocolatey_path =
"#{ENV['SYSTEMDRIVE']}\\ProgramData\\chocolatey\\bin"
windows_path 'update_path_for_system' do
action :add
path
chocolatey_path
end
ruby_block 'add_chocolatey_path' do
block do
new_path =
"#{ENV['PATH']};#{chocolatey_path}"
ENV['PATH']
= "#{ENV['PATH']};#{new_path}"
end
not_if {
(ENV['PATH'].split(';').collect
{ | element | element.downcase }).include? chocolatey_path.downcase
}
end
powershell_script 'chocolatey_install' do
code
<<-eoh o:p="">
powershell -noprofile -inputformat none
-noninteractive -executionpolicy bypass -command "iex ((new-object
net.webclient).DownloadString('https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))"
EOH
# not_if {
ChocolateyHelpers::chocolatey_installed? }
not_if
"test-path '#{chocolatey_path}\\choco.exe'"
end
The above recipe will
install chocolatey on the workstation if not present.
Step 6: Setup PowerShell and WinRM
Similarly create a new recipe and name it setuppowershell. Add
the below code to the setuppowershell.rb file.
#
# Cookbook Name:: windowsdev
# Recipe:: setuppowershell
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 Prajeesh Prathap, All Rights
Reserved.
powershell_script 'ExecutionPolicyUnrestricted' do
code
<<-eoh o:p="">
powershell -noprofile -executionpolicy bypass -command
{set-executionpolicy unrestricted -force -scope localmachine}
exit 0
EOH
only_if
"(get-executionpolicy -scope localmachine) -ne 'unrestricted'"
end
powershell_script 'ExecutionPolicyUnrestrictedX86' do
architecture
:i386 # Handle 32-bit Powershell (no-op
if OS is 32-bit)
code
<<-eoh o:p="">
powershell -noprofile -executionpolicy bypass -command
{set-executionpolicy unrestricted -force -scope localmachine}
exit 0
EOH
only_if
"(get-executionpolicy -scope localmachine) -ne 'unrestricted'"
end
powershell_script 'Setup WINRM' do
code
<<-eoh o:p="">
Set-WSManQuickConfig -Force
EOH
flags
'-NoLogo, -NonInteractive, -NoProfile, -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted'
end
Step 7: Add extra files or scripts
If you want to add
some custom scripts and execute them as part of the run list, then you can include
them in the files directory of the cookbook and refer to those in the recipes.
To add a custom
powershell script to the cookbook, use the chef generate file command as given
below
Chef generate file
configure_psmodules.ps1
Open the script file
in the editor and paste the code given below and save it. This will install
some modules from the PowerShell gallery to the machine.
Install-Module -Name xPSDesiredStateConfiguration
-Force
Install-Module -Name xDSCResourceDesigner -Force
Install-Module
-Name PSScriptAnalyzer –Force
Step 8: Use the script file in the
recipe
We can also execute
the code from the script files that we included as part of the cookbook. To
execute the configure_psmodules.ps1 file, we’ll now make the changes to the
setuppowershell recipe and add the following lines below
cookbook_file "#{ENV['USERPROFILE']}/configure_psmodules.ps1"
do
source
'configure_psmodules.ps1'
end
powershell_script "Run code from script to
install modules" do
code
"#{ENV['USERPROFILE']}/configure_psmodules.ps1"
end
This will copy the
file to the users folder and then execute the file.
Step 10: Install chocolatey packages
Create a new recipe
and name it chocopackages. This recipe will be used to mention all the
chocolatey packages needed for the machine.
Add the code to the
recipe, to install the chocolatey packages
#
# Cookbook Name:: windowsdev
# Recipe:: chocopackages
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 Prajeesh Prathap, All Rights
Reserved.
include_recipe 'chocolatey'
chocolatey 'Fiddler'
chocolatey 'SublimeText2'
chocolatey '7zip.install'
chocolatey 'freemind'
chocolatey 'javaruntime'
chocolatey 'jre8'
chocolatey 'picpick.portable'
chocolatey 'adobereader'
chocolatey 'github'
chocolatey 'sysinternals'
chocolatey 'procexp'
chocolatey 'pester'
chocolatey 'beyondcompare'
chocolatey 'ilspy'
chocolatey 'ncrunch-vs2015'
chocolatey
'ProcessExplorer'
Step 11: Linking it all together
We have a list of
recipes to be executed as part of the run. But before we start, we need to link
all these recipes in the default.rb recipe of the cookbook. You can use the
include statement to add the recipes to be executed in the cookbook. Open the default.rb
file and add the below lines of code.
#
# Cookbook Name:: windowsdev
# Recipe:: default
#
# Copyright (c) 2016 Prajeesh Prathap, All Rights
Reserved.
# Call all recipies from here
if node['platform'] == "windows"
include_recipe
'windowsdev::setupchoco'
include_recipe
'windowsdev::setuppowershell'
include_recipe
'windowsdev::configurereg'
include_recipe
'windowsdev::chocopackages'
end
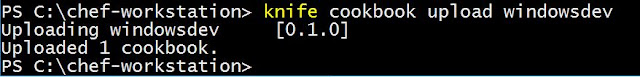
Step 12: Upload the cookbook to chef
server
To upload the cookbook
to the chef server you can use the knife cookbook upload [[cookbookname]]
command.
Knife cookbook upload
windowsdev
Step 13: Adding a new role to the
chef server with cookbook
We’ll create a new
Role with name devmachine and use the recipe windowsdev in the run list. Later
when we bootstrap the node, we’ll use this role so that our recipe will be used
to configure the node.
To create a role file,
in the code editor add a new file name devmachine.json under the roles folder
in the chef repository. Open the JSON file and add the contents below.
{
"name": "devmachine",
"description": "Configures a windows development
machine",
"chef_type": "role",
"json_class": "Chef::Role",
"default_attributes": {
},
"override_attributes": {
},
"run_list": [
"recipe[windowsdev]"
]
}
Knife role from file .\roles\devmachine.json
You can view the role
and details in the chef server also.
Step 14: Bootstrapping the node
A bootstrap is a
process that installs the chef-client on a target system so that it can run as
a chef-client and communicate with a Chef server. We can use the knife
bootstrap command to bootstrap our node and use the devmachine role as the run list.
knife bootstrap
windows winrm 127.0.0.1 --node-name ‘YOUR_NODENAME’ -r 'role[devmachine]'
Please note that you
have to configure your winrm username and password in the knife.rb file to get
this working.
And that's all! You
are now able to setup a development machine with all the basic software and
configuration you need. The final structure and the files used in this sample
can be found at my Github repository (https://github.com/prajeeshprathap/chefdev)
. Go ahead and play with it!!!!















No comments:
Post a Comment